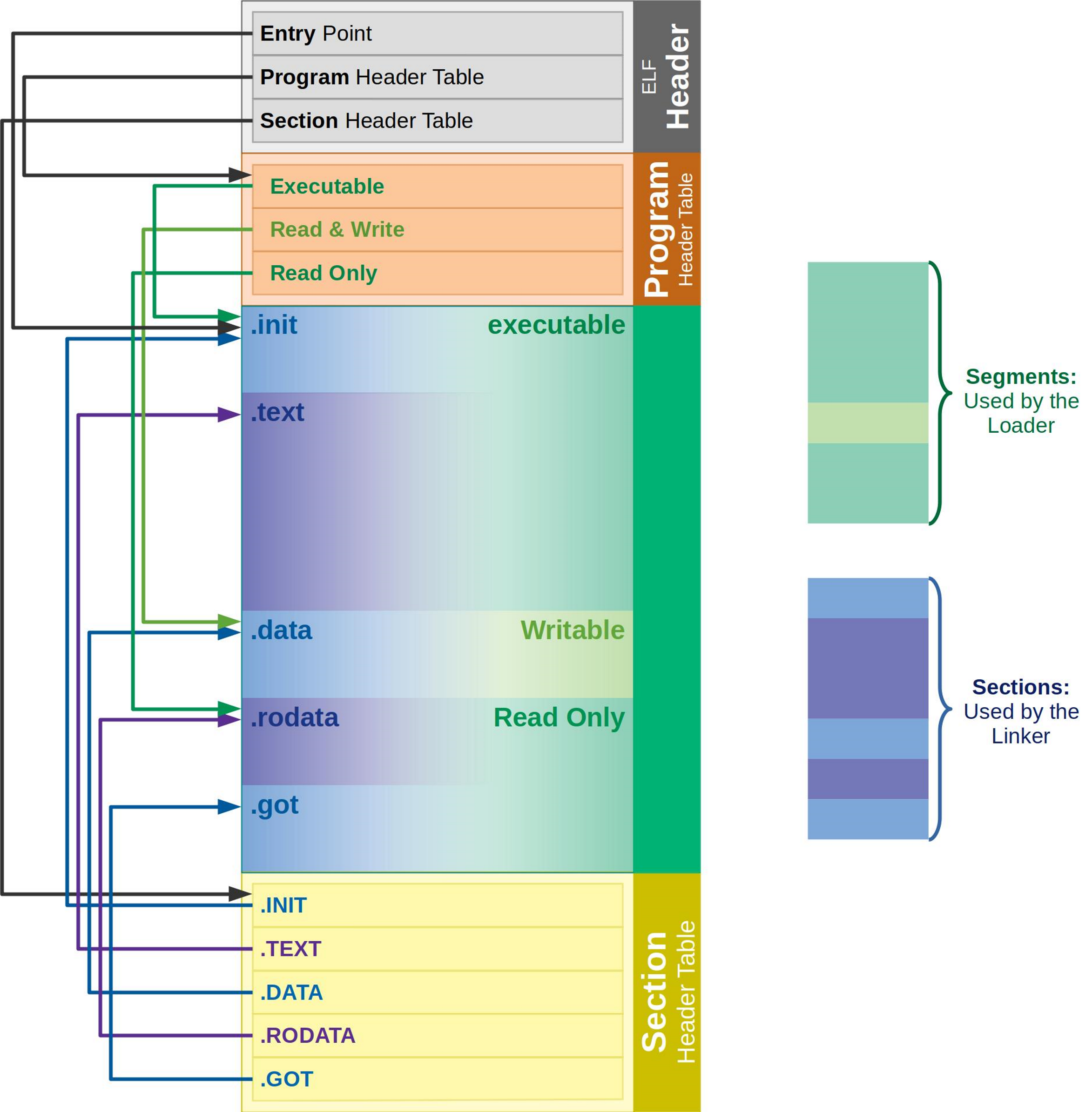
ELF Format(Executable and Linkable Format)은 각 영역(TEXT, DATA, BSS등)을 정의하여 프로그램이 실행 시에 이 영역들을 메모리에 올리기 위해 사용됩니다.
ELF Format의 File은 여러 segments와 sections로 구성되며, 단일 segment는 여러 section으로 구성될 수 있습니다.
ELF Format에는 ELF header, Program header, Section header가 존재하며 이를 통해 각 영역들을 확인할 수 있습니다.
아래에서는 위에서 언급한 각 header에 대해서 보다 상세하게 알아보도록 하겠습니다.
1. ELF header
ELF Format File의 맨 처음에 위치하며, Program header와 Section header위치는 ELF header에서 확인 가능합니다.
ELF header의 구조체와 각 필드 값의 이미는 다음 경로에서 확인 가능합니다.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Executable_and_Linkable_Format
https://refspecs.linuxfoundation.org/elf/gabi4+/ch4.eheader.html
테스트로 작성한 파일에 대해서 readelf 도구를 통해 ELF header 정보를 확인해보겠습니다.
예제1) 실행 파일
hwjung@jhaewon-z01:~$ readelf -h helloworld
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF64
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI Version: 0
Type: DYN (Shared object file)
Machine: Advanced Micro Devices X86-64
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0x1060
Start of program headers: 64 (bytes into file)
Start of section headers: 14720 (bytes into file)
Flags: 0x0
Size of this header: 64 (bytes)
Size of program headers: 56 (bytes)
Number of program headers: 13
Size of section headers: 64 (bytes)
Number of section headers: 31
Section header string table index: 30
예제2) 오브젝트 파일
hwjung@jhaewon-z01:~$ readelf -h functionA.o
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF64
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI Version: 0
Type: REL (Relocatable file)
Machine: Advanced Micro Devices X86-64
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0x0
Start of program headers: 0 (bytes into file)
Start of section headers: 608 (bytes into file)
Flags: 0x0
Size of this header: 64 (bytes)
Size of program headers: 0 (bytes)
Number of program headers: 0
Size of section headers: 64 (bytes)
Number of section headers: 12
Section header string table index: 11
위에서 테스트로 확인한 ELF header 내용에 대해서 하나씩 살펴보도록 하겠습니다.
먼저, ELF header에 해당하는 구조체는 다음과 같이 정의되어 있습니다.
#define EI_NIDENT 16
typedef struct {
unsigned char e_ident[EI_NIDENT];
Elf32_Half e_type;
Elf32_Half e_machine;
Elf32_Word e_version;
Elf32_Addr e_entry;
Elf32_Off e_phoff;
Elf32_Off e_shoff;
Elf32_Word e_flags;
Elf32_Half e_ehsize;
Elf32_Half e_phentsize;
Elf32_Half e_phnum;
Elf32_Half e_shentsize;
Elf32_Half e_shnum;
Elf32_Half e_shstrndx;
} Elf32_Ehdr;
각 구조체 안에 변수들이 나타내는 값은 다음과 같습니다.
1) e_ident[EI_NIDENT]
| Offset | Size | Index | Definition | Value |
| 0x00 | 4bytes | File identification | magic number | 7F 45('E') 4C('L') 46('F') |
| 0x04 | 1bytes | e_ident[EI_CLASS] | file's class | 1(32bit) or 2(64bit) |
| 0x05 | 1bytes | e_ident[EI_DATA] | encoding of both the data structures | 1(LSB) or 2(MSB) |
| 0x06 | 1bytes | e_ident[EI_DATA] | ELF header version number | this value must be EV_CURRENT |
| 0x07 | 1bytes | e_ident[EI_OSABI] | OS- or ABI-specific ELF extensions | 0 can also be taken to mean unspecified |
| 0x08 | 1bytes | e_ident[EI_ABIVERSION] | version of the ABI | value 0 shall be used |
| 0x09 | 7bytes | e_ident[EI_PAD] | beginning of the unused bytes in e_ident | These bytes are reserved and set to zero |
2) e_type : ELF File Type
| Name | Value | Meaning |
| ET_NONE | 0 | No file type |
| ET_REL | 1 | Relocatable file |
| ET_EXEC | 2 | Executable file |
| ET_DYN | 3 | Shared object file |
| ET_CORE | 4 | Core file |
3) e_machine : CPU Architecture
| Name | Value | Meaning |
| EM_386 | 0x3 | Intel 80386 |
| EM_X86_64 | 0x3e | AMD x86-64 architecture |
4) e_version : ELF File Version
5) e_entry : Virtual Memory Entry Point
6) e_phoff : Program header table file offset
7) e_shoff : Section header table file offset
8) e_flags : processor specific flags
9) e_ehsize : ELF header 크기
10) e_phentsize : Program header table entry 크기
11) e_phnum : Program header table entry 갯수
12) e_shentsize : Section header table entry 크기
13) e_shnum : Section header table entry 갯수
14) e_shstrndx : String table section과 연관된 entry의 section header table index
Hexdump를 이용하여, helloworld 파일을 16진수로 출력해보면 ELF header 정보를 Mapping 시켜볼 수 있습니다.
먼저, 다시 readelf 도구로 ELF header를 조회하고 Hexdump로 helloword 파일을 16진수로 조회합니다.
hwjung@jhaewon-z01:~$ readelf -h helloworld
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF64
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI Version: 0
Type: DYN (Shared object file)
Machine: Advanced Micro Devices X86-64
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0x1060
Start of program headers: 64 (bytes into file)
Start of section headers: 14712 (bytes into file)
Flags: 0x0
Size of this header: 64 (bytes)
Size of program headers: 56 (bytes)
Number of program headers: 13
Size of section headers: 64 (bytes)
Number of section headers: 31
Section header string table index: 30hwjung@jhaewon-z01:~$ hexdump -C helloworld | head
00000000 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |.ELF............|
00000010 03 00 3e 00 01 00 00 00 60 10 00 00 00 00 00 00 |..>.....`.......|
00000020 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 78 39 00 00 00 00 00 00 |@.......x9......|
00000030 00 00 00 00 40 00 38 00 0d 00 40 00 1f 00 1e 00 |....@.8...@.....|
00000040 06 00 00 00 04 00 00 00 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |........@.......|
00000050 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 40 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |@.......@.......|
00000060 d8 02 00 00 00 00 00 00 d8 02 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000070 08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 03 00 00 00 04 00 00 00 |................|
00000080 18 03 00 00 00 00 00 00 18 03 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000090 18 03 00 00 00 00 00 00 1c 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
readelf 조회 정보와 Hexdump 조회 결과를 비교하면 다음과 같이 그려볼 수 있습니다.
위에서는 32bit 구조체를 살펴보았지만 본 예제는 64bit로 작성된 프로그램을 조회한 것이기 때문에 각 Fileld의 사이즈를 고려해야 합니다.
// 64-bit ELF header. Fields are the same as for ELF32, but with different
// types (see above).
struct Elf64_Ehdr {
unsigned char e_ident[EI_NIDENT];
Elf64_Half e_type;
Elf64_Half e_machine;
Elf64_Word e_version;
Elf64_Addr e_entry;
Elf64_Off e_phoff;
Elf64_Off e_shoff;
Elf64_Word e_flags;
Elf64_Half e_ehsize;
Elf64_Half e_phentsize;
Elf64_Half e_phnum;
Elf64_Half e_shentsize;
Elf64_Half e_shnum;
Elf64_Half e_shstrndx;
bool checkMagic() const {
return (memcmp(e_ident, ElfMagic, strlen(ElfMagic))) == 0;
}
unsigned char getFileClass() const { return e_ident[EI_CLASS]; }
unsigned char getDataEncoding() const { return e_ident[EI_DATA]; }
};

다음은 각 Segment에 대한 정보를 담고 있는 Program header에 대해서 알아보겠습니다.
'Debugging > Linux' 카테고리의 다른 글
| CPU Registers and Instructions - Instructions (0) | 2022.11.05 |
|---|---|
| CPU Registers and Instructions - Registers (0) | 2022.11.03 |
| 64bit Stack Walking (0) | 2022.10.14 |
| ELF Format #3 - Section Header (0) | 2022.10.09 |
| ELF Format #2 - Program Header (0) | 2022.10.08 |


